White Beans in the Diet: White Beans Nutrition Facts
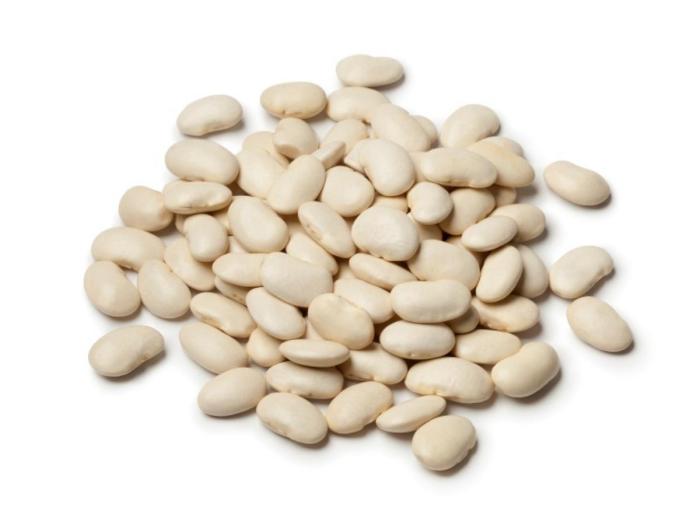

White beans nutrition facts – White beans are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a wealth of health benefits and culinary versatility. Their high protein and fiber content contribute to satiety, aiding in weight management and promoting digestive health. This section explores diverse ways to incorporate white beans into your diet, from creative recipes to practical meal planning and storage tips.
Three White Bean Recipes
White beans lend themselves beautifully to a variety of cuisines. Their mild flavor allows them to absorb other tastes, making them an ideal ingredient for both simple and sophisticated dishes. Below are three recipes showcasing their versatility.
White beans are a nutritional powerhouse, boasting high fiber and protein content. It’s interesting to compare their nutritional profile to something quite different, like the krispy kreme nutrition facts , which highlight the stark contrast in sugar and fat content. Returning to white beans, their low glycemic index makes them a healthier choice for sustained energy levels.
- Simple White Bean and Roasted Vegetable Salad:
- Ingredients: 1 can (15 ounces) cannellini beans, rinsed and drained; 1 cup roasted vegetables (e.g., broccoli, bell peppers, zucchini); 1/4 cup red onion, thinly sliced; 2 tablespoons olive oil; 2 tablespoons lemon juice; 1 teaspoon dried oregano; salt and pepper to taste.
- Instructions: Combine all ingredients in a bowl. Toss gently to combine. Season with salt and pepper. Serve chilled or at room temperature.
- Creamy White Bean and Spinach Soup:
- Ingredients: 1 tablespoon olive oil; 1 onion, chopped; 2 cloves garlic, minced; 4 cups vegetable broth; 2 cups fresh spinach; 1 can (15 ounces) cannellini beans, rinsed and drained; 1/2 cup heavy cream or coconut cream (for vegan option); salt and pepper to taste.
- Instructions: Sauté onion and garlic in olive oil until softened. Add vegetable broth and bring to a boil. Stir in spinach and beans. Simmer until spinach is wilted. Blend until smooth.
Stir in cream and season with salt and pepper. Serve hot.
- White Bean and Sausage Stew:
- Ingredients: 1 pound Italian sausage, removed from casings; 1 onion, chopped; 2 carrots, chopped; 2 celery stalks, chopped; 4 cups vegetable broth; 2 cans (15 ounces each) cannellini beans, rinsed and drained; 1 teaspoon dried rosemary; 1/2 teaspoon dried thyme; salt and pepper to taste.
- Instructions: Brown sausage in a large pot. Add onion, carrots, and celery and cook until softened. Stir in vegetable broth, beans, rosemary, and thyme. Bring to a simmer and cook for 15-20 minutes, or until flavors have melded. Season with salt and pepper.
Serve hot with crusty bread.
One-Week White Bean Meal Plan
Incorporating white beans into your weekly meals is easy and beneficial. This sample meal plan demonstrates diverse ways to enjoy them. Portion sizes are approximate and can be adjusted based on individual needs.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with 1/2 cup white beans, berries, and nuts | White bean and roasted vegetable salad (recipe above) | White bean and sausage stew (recipe above) |
| Tuesday | Yogurt with 1/4 cup white beans, granola, and fruit | Leftover white bean and sausage stew | Lentil soup with a side of 1/2 cup white beans |
| Wednesday | Scrambled eggs with 1/4 cup white beans and spinach | Sandwich on whole-wheat bread with mashed white beans and vegetables | Pasta with white bean sauce and vegetables |
| Thursday | Smoothie with 1/2 cup white beans, banana, and spinach | Leftover pasta with white bean sauce | Chicken and white bean chili |
| Friday | Toast with mashed white beans and avocado | White bean dip with vegetables and crackers | Pizza with white bean base and vegetables |
| Saturday | Breakfast burrito with scrambled eggs and 1/4 cup white beans | Salad with grilled chicken and 1/2 cup white beans | White bean burgers on whole-wheat buns |
| Sunday | Pancakes with 1/4 cup white beans and fruit | Leftover white bean burgers | Creamy white bean and spinach soup (recipe above) |
Preparing and Storing White Beans, White beans nutrition facts
Proper preparation and storage are crucial for maximizing the flavor and nutritional value of white beans.
- Canned White Beans:
- Rinse thoroughly before use to remove excess sodium.
- Can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 5 days after opening.
- Dried White Beans:
- Sort and rinse beans to remove any debris.
- Soak beans in cold water for at least 6-8 hours, or overnight.
- Drain and rinse soaked beans before cooking.
- Cook beans in plenty of water until tender, usually 45-60 minutes.
- Store cooked beans in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 5 days.
- Dried beans can be stored in a cool, dry place for up to a year.
White Beans in Diverse Cuisines and Diets
White beans are incredibly adaptable and easily integrated into various culinary traditions and dietary approaches. They are a staple in Mediterranean cuisine, often featured in stews, salads, and dips. Their high protein content makes them a valuable addition to vegetarian and vegan diets, providing a plant-based protein source. They can also be incorporated into many other cuisines, such as Mexican, Indian, and Italian dishes.
The versatility of white beans allows for countless possibilities in the kitchen, making them a beneficial and delicious addition to any balanced diet.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
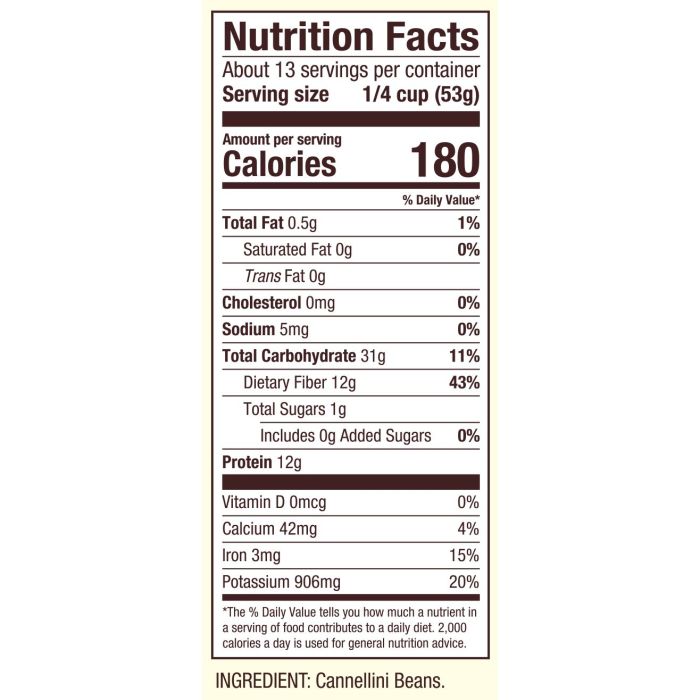
While white beans offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential drawbacks and consider individual circumstances. Certain components within white beans, as well as their high fiber content, can affect some individuals differently. Understanding these potential issues allows for informed consumption and mitigation of any adverse effects.
Antinutrient Content and Mitigation
White beans, like many legumes, contain antinutrients such as phytic acid and lectins. Phytic acid can bind to minerals, reducing their absorption, while lectins may interfere with digestion in some individuals. However, these effects can be significantly reduced through proper food preparation. Soaking the beans in water for several hours, or even overnight, before cooking helps to break down these antinutrients.
Thorough cooking, preferably by boiling, further diminishes their presence. This simple preparation significantly enhances the bioavailability of nutrients in white beans.
Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
White beans’ high fiber content can affect the absorption of certain medications. For example, individuals taking medications for diabetes or blood thinners should consult their doctor about potential interactions. Similarly, people with pre-existing digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may need to adjust their white bean intake gradually to assess their tolerance. Individual responses vary, and consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended for personalized guidance.
Digestive Issues Associated with High Fiber Intake
The high fiber content in white beans, while beneficial for gut health in many, can also lead to digestive discomfort in others. Symptoms like gas, bloating, and flatulence are common, particularly when consuming large quantities of white beans without proper preparation or gradual introduction into the diet. Starting with smaller portions and increasing intake gradually allows the gut microbiome to adapt.
Combining white beans with other foods, drinking plenty of water, and incorporating probiotic-rich foods can help alleviate digestive issues.
Potential Allergic Reactions
Although less common than allergies to other legumes like peanuts or soybeans, allergic reactions to white beans are possible. Symptoms can range from mild, such as skin rash or itching, to more severe reactions like hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. In case of a suspected allergic reaction, immediate medical attention is crucial. Individuals with known legume allergies should exercise caution and potentially avoid white beans altogether.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are white beans good for weight loss?
Yes, their high fiber and protein content promote satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer and potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
Can I eat white beans every day?
While generally safe, daily consumption might lead to digestive discomfort for some due to the high fiber content. Moderation is key.
How long can I store cooked white beans?
Cooked white beans should be stored in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 3-4 days.
Are there any interactions between white beans and medications?
White beans can potentially interact with certain medications, particularly those affecting blood sugar levels. Consult your doctor if you have concerns.
What are the best ways to reduce gas from white beans?
Soaking dried beans overnight and properly cooking them can significantly reduce gas-producing compounds.